This section of the toolkit focuses on support for teaching and learning in mathematics. It explores the connection between teaching and learning in mathematics and numeracy.
Mathematics and numeracy
Numeracy and mathematics are not synonymous (DEETYA, 1997).
Although the terms numeracy, mathematics and mathematical literacy are often used interchangeably (Groves et al., 2006), it is important to differentiate between these two ideas and consider what this means for the teaching of mathematics and learning numeracy.
Mathematics in the early years
Young children learn from watching and listening and engaging with the world around them. New skills and understandings can emerge through demonstration, modelling and problem-solving. In early years settings, educators enrich learning activities by using mathematical language that helps children to explore, describe and understand the world around them and builds strong foundations for future learning in mathematics.
Evidence shows that the use of high-quality curriculum resources, together with pedagogy that responds to and adapts to the needs of students leads to increased engagement and improved student outcomes.
Mathematics in the classroom
In mathematics classrooms, it is important to create a rich learning environment that encourages a positive mindset and opens up the potential for growth in mathematics teaching and learning.
Using a range of teaching strategies that connect the content, skills and concepts will enhance understanding and engagement and build students’ confidence as mathematics learners and thinkers.
In the mathematics classroom, students are exposed to opportunities that help them to:
- develop and engage their mathematical thinking
- solve problems and demonstrate their understanding
- apply strategies and conceptual understanding in familiar and unfamiliar situations
- recognise the relevance of their experiences in their environment through a mathematical lens
- use and connect what they are learning to contexts outside the mathematics classroom.
Teachers help students to engage with, explore and make connections between their mathematical knowledge, skills and understandings with other learning areas and the world around them.
The proficiencies
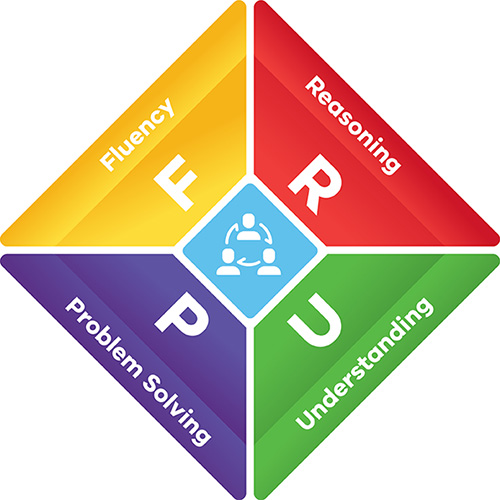
The Victorian Curriculum: Mathematics identifies the fundamental relationship between learning in mathematics and numeracy. This relationship is demonstrated and reinforced across the strands of the mathematics curriculum and in the teaching and learning program through the
proficiencies:
- understanding
- fluency
- problem-solving
- reasoning.
Curriculum planning
Curriculum planning is fundamental to developing an engaging and effective mathematics and numeracy teaching and learning program in schools and early learning centres.
Incorporating numeracy into
planning across the curriculum helps students become more proficient in all aspects of numeracy. Students can then make meaningful connections with a range of real-world contexts.
Teaching practice and supports
These
resources and support materials help teachers build confidence and capacity to develop and deliver quality teaching and learning programs.
Additional resources
A collection of multimodal resources to support planning, teaching and assessment in mathematics and improve outcomes in mathematics classrooms.
Animations to support families engage in conversations about mathematics and numeracy in everyday environments.
Provides teachers with content knowledge, suggested teaching and learning ideas as well as links to other resources, including sample planning templates. Resources are organised by Mathematics strands and sub-strands and incorporate the proficiencies: understanding, fluency, problem-solving and reasoning.
Resources to support the teaching of mathematics and numeracy from Foundation to Level 10. Resources are aligned to the Victorian curriculum frameworks. Digital resource packages are also available.
A unique suite of activities for all school-aged children. The activities engage students in fun ways to use mathematics with their families.
Designed to promote creativity, problem-solving, critical thinking, and collaboration between students. Explore mathematical concepts such as spatial reasoning, measurement, location and space through Minecraft worlds.
Activities and resources aligned to the Victorian curriculum. Includes teaching ideas, activities, videos, PowerPoint presentations and worksheets.
A range of classroom activities including a mathematics activity on scale that covers Levels 4 to 8 of the Victorian Curriculum. Includes lesson plans, student worksheets and instructions to support the investigation of the Mini Melbourne world.
Available for secondary and P-12 government schools. Includes curriculum-aligned videos, animations and mini clips to support teaching and learning in mathematics and numeracy. An information pack for parents is also available.
A guide that explores the mathematical beauty of key landmarks, structures and architecture in Melbourne. The app provides different maths trails that you can enjoy exploring in Melbourne or in your own neighbourhood.
References
Department of Employment, Education, Training and Youth Affairs. [DEETYA] (1997). Numeracy = Everyone’s Business: The report of the numeracy education strategy development conference. Canberra: Australian Association of Mathematics Teachers.
Groves, S., Mousley, J., & Forgasz, H. (2006). Primary numeracy: A mapping, review and analysis of Australian research in numeracy learning at the primary school level. Canberra: Department of Education, Science and Training.